What had been the outstanding outcomes of a crossover examine randomizing tons of of individuals with diabetes to 1 and a 3rd cups of millet day-after-day?
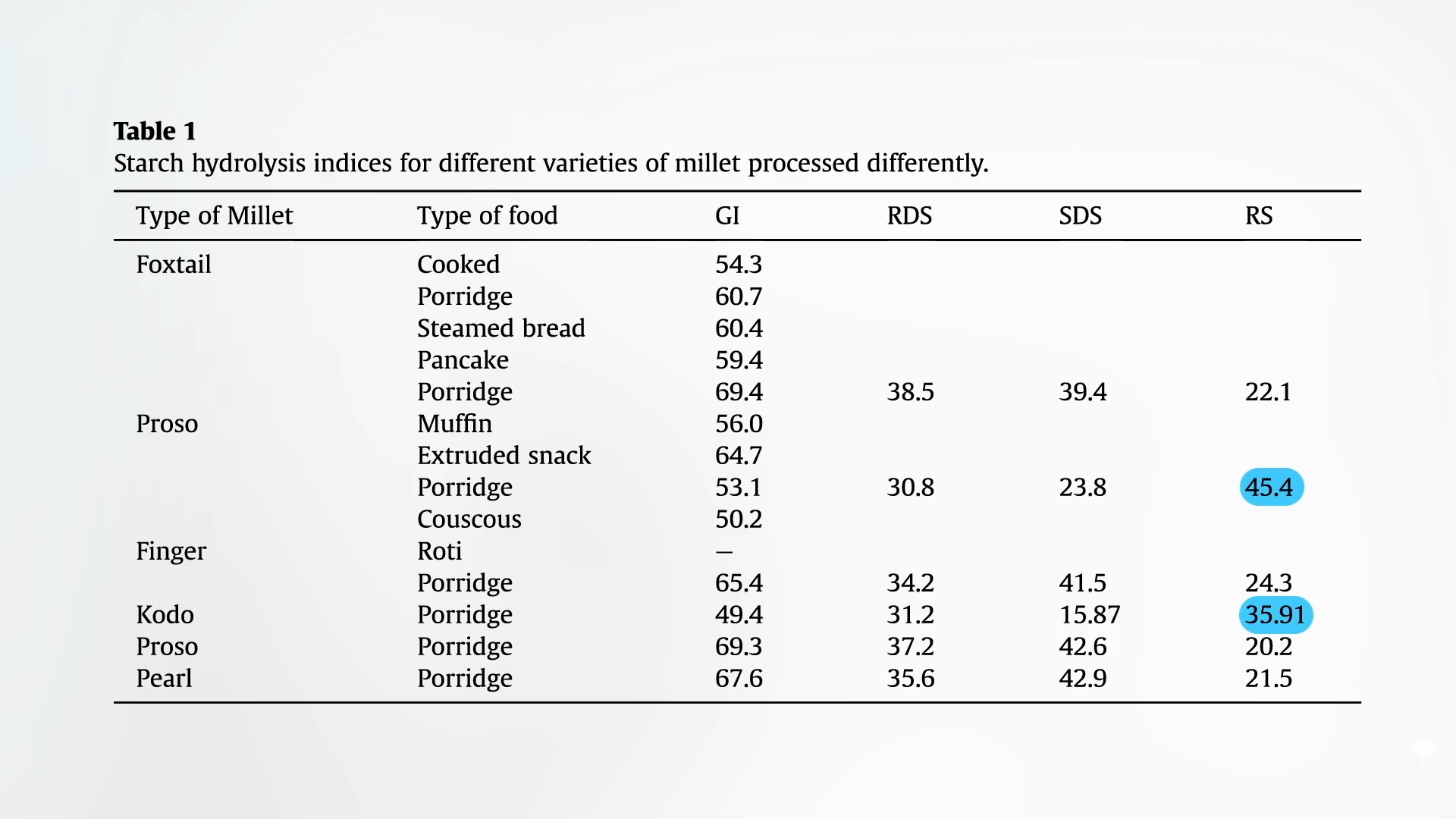
How does millet come to the assistance of individuals with diabetes? A considerable portion of the starch in millet is resistant starch, which means it’s proof against digestion in our small gut so it offers a bounty for the nice bugs in our colon. Under and at 0:28 in my video The Advantages of Millet for Diabetes is a desk displaying how the varied millets do. As you possibly can see, they’re all a lot greater in resistant starch than extra widespread grains, like rice or wheat, however proso and kodo millets lead the pack.
What’s happening? The protein matrix in millet not solely acts as a bodily barrier but in addition partially sequesters our starch-munching enzyme, and the polyphenols in millet can even act as starch blockers themselves.
Millet has markedly slower abdomen emptying instances than different starchy meals, too. After we eat white rice, boiled potatoes, or pasta, our abdomen takes about an hour to digest it, earlier than it begins to slowly launch it into our intestines, and it takes about two or three hours to empty about midway. After we eat sorghum or millet, although, abdomen emptying doesn’t even begin for 2 or three hours and it might take 5 hours to empty simply midway, as you possibly can see beneath and at 1:22 in my video.
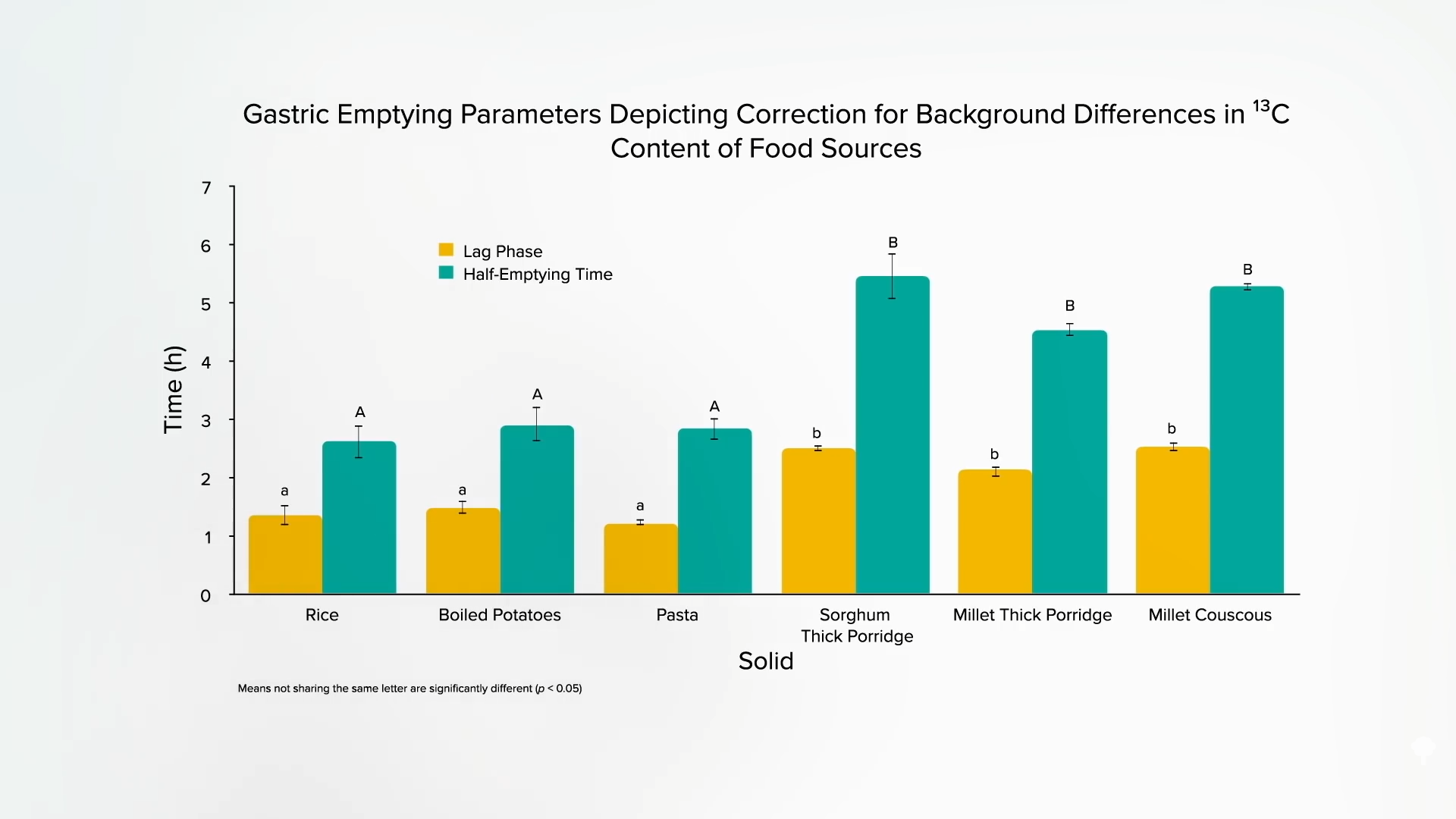
Notice that this was the case with each a thick millet porridge and a millet couscous. “The non-viscous millet couscous meal was additionally equally sluggish in [stomach] emptying. This means that there’s an intrinsic property” of millet itself that helps decelerate the speed of abdomen emptying, which ought to blunt the blood sugar spike. What occurred when it was put to the take a look at?
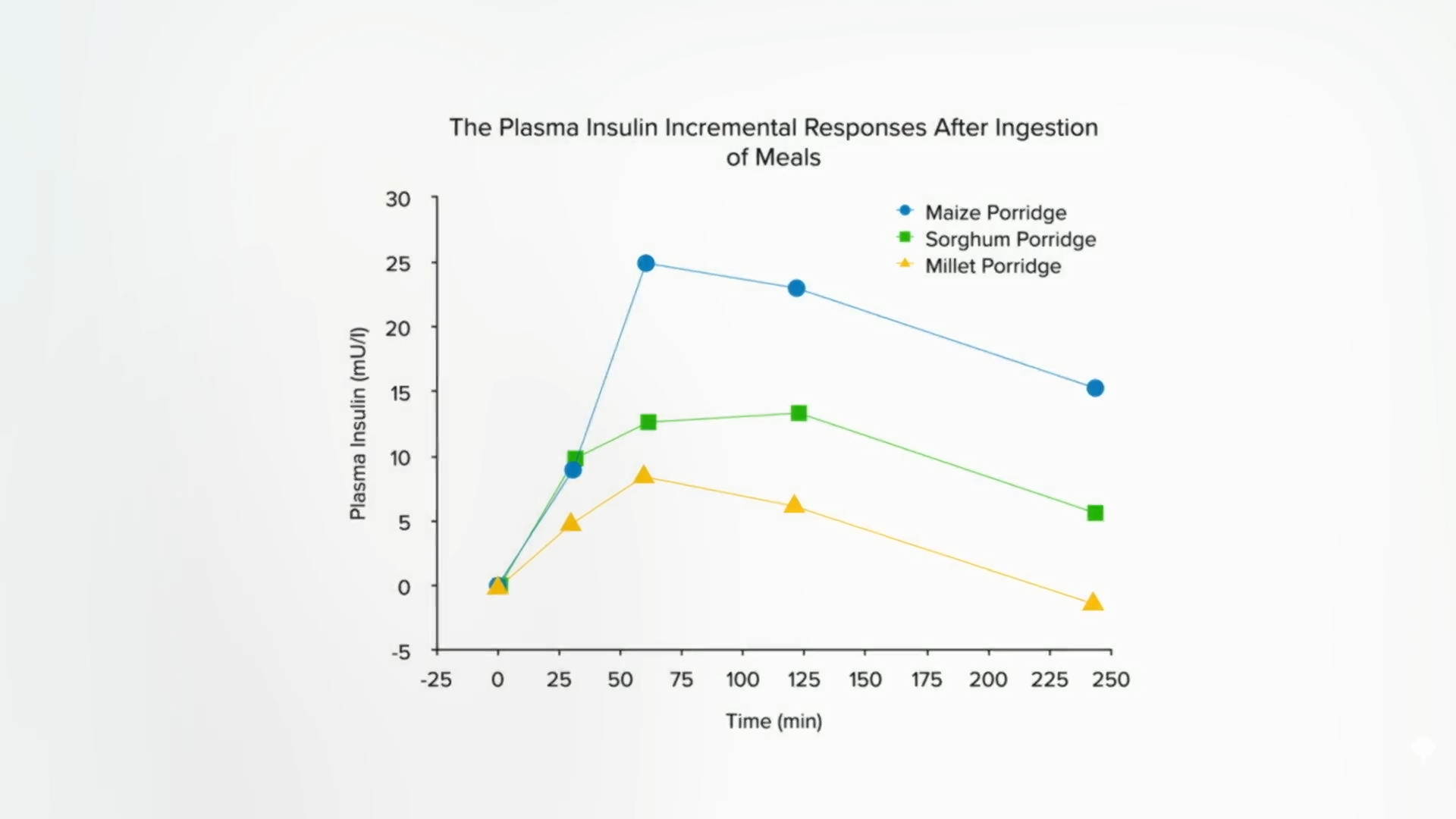
Certainly, millet brought on a couple of 20 p.c decrease surge in blood sugar than the identical quantity of carbohydrates within the type of rice. Bear in mind how excited I used to be to present you the way it solely took the physique about half the insulin to deal with sorghum in comparison with a grain like corn? Nicely, millet did even higher, as seen right here and at 2:07 in my video.
When a gaggle of prediabetic people had been given about three quarters of a cup of millet a day, inside six weeks, their insulin resistance dropped a lot that their prediabetic fasting blood sugars was non-prediabetic blood sugars, as proven beneath and at 2:22 in my video.
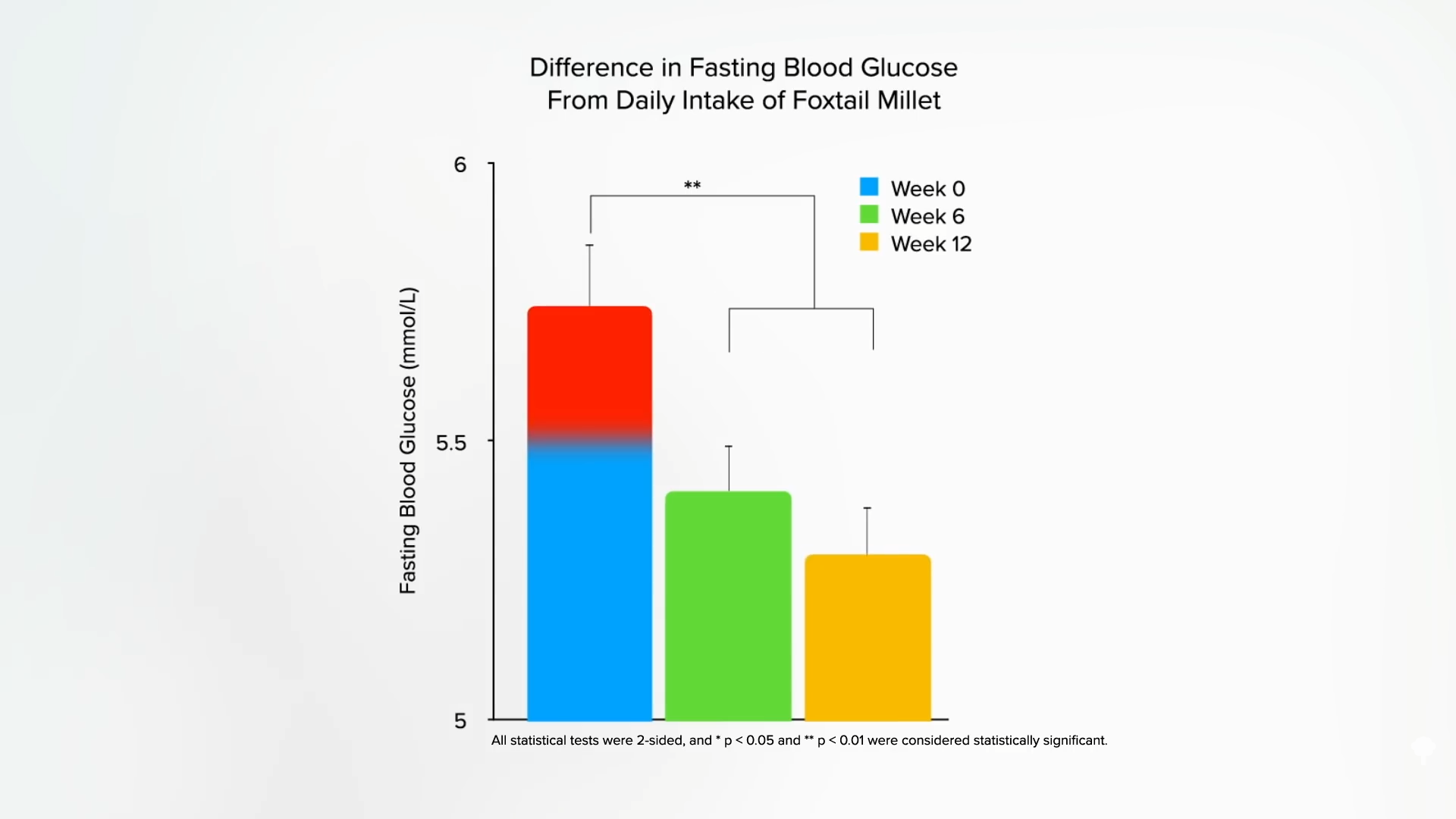
This “self-controlled scientific trial,” with the identical topics earlier than and after, is only a sneaky means of claiming it’s an uncontrolled trial. There was no management group through which individuals both didn’t add the millet or added one thing else, and we all know that simply being below scrutiny in a examine could cause folks to eat higher in different methods. So, we don’t know what position, if any, the millet itself performed. What we’d like is a randomized, managed, crossover trial the place the identical folks eat diets with and with out millet so we will see which works higher. And right here we go: a randomized, crossover examine with tons of of sufferers following an American Diabetes Affiliation-type weight-reduction plan with and with out about one and a 3rd cups of millet day-after-day. Researchers discovered that the millet-based weight-reduction plan lowered hemoglobin A1C ranges, which means there was an enchancment in long-term blood sugar management, in addition to the achievement of some aspect advantages like decreasing ldl cholesterol.
The goal for good blood sugar management really helpful by the American Diabetes Affiliation is an A1C of lower than 7. The individuals began out at 8.37, however after just a few months on millet, their A1C dropped to a median of 6.77, as seen right here and at 3:35 in my video.
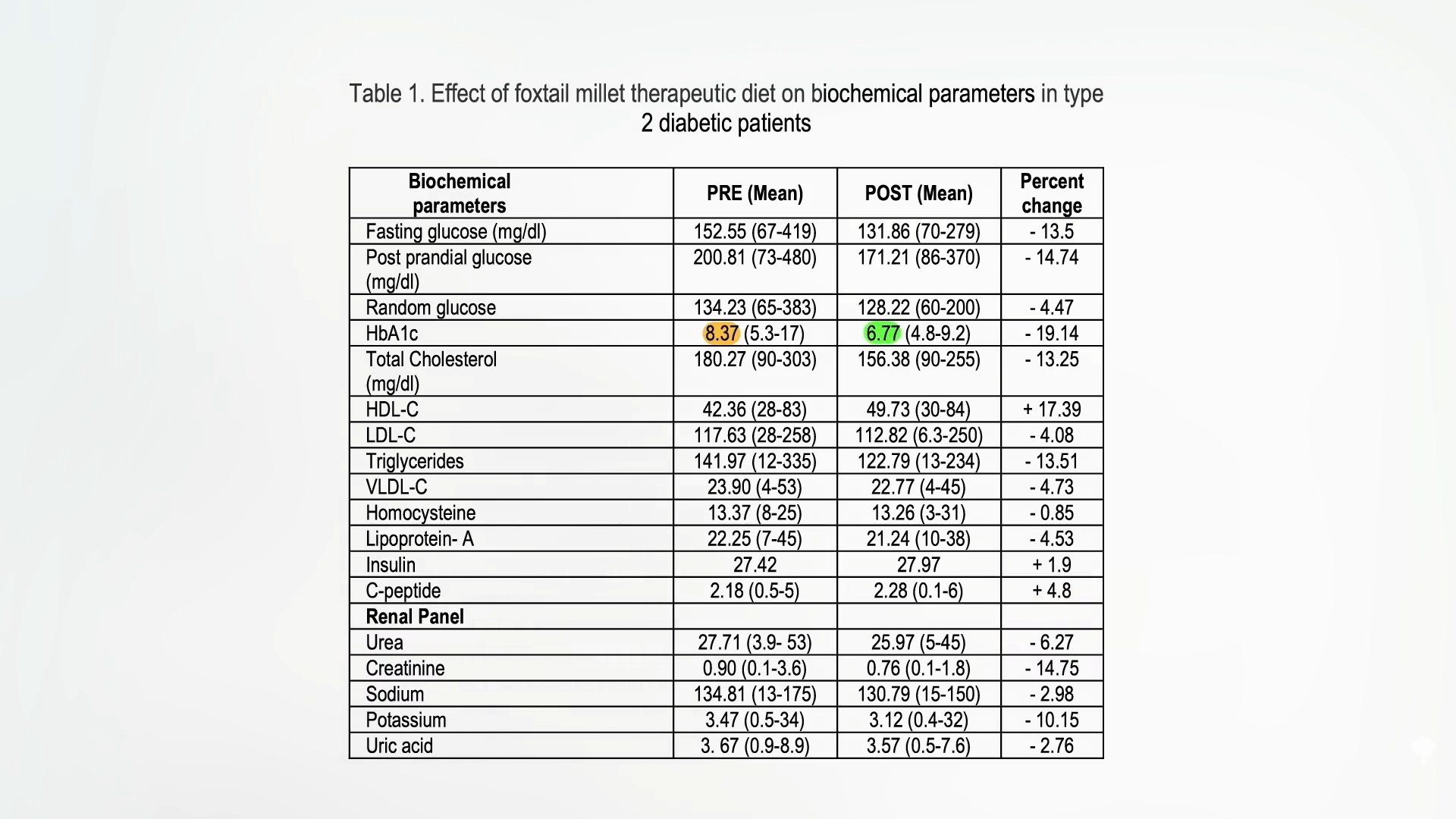
Is it simply because they misplaced weight? No, which suggests it was an impact particular to the millet. The researchers didn’t simply give them millet, although. They blended the millet with break up black lentils and spices, and we all know from dozens of randomized, managed experimental trials in folks with and with out diabetes that consuming pulses—beans, break up peas, chickpeas, and lentils—can enhance long-term measures of blood sugar management like A1C ranges. So, whereas the researchers “concluded that millets do have a possible for a protecting position within the administration of diabetes,” a extra correct conclusion could be a mixture of millets and lentils will be protecting. The spices could have helped, too. The researchers didn’t say which spices had been used, and I couldn’t get involved with the authors, however the same examine carried out by one of many similar researchers included a couple of every day tablespoon of a combination of fenugreek, coriander, cumin, and black pepper, with a fifth spice, maybe cinnamon or turmeric.









Discussion about this post